Published on: September 7, 2022 | Updated on: January 18, 2025
Severe knee injuries can cause loss of full motion in your knee. As a result, you feel unbearable pain when trying to straighten your leg.
Knee pain has varying causes and intensities. For instance, you may not straighten your knee because you feel like something is blocking it from moving. Another reason could be severe pain and swelling from an injury when you extend your knee.
The treatment of knee injuries depends on your lifestyle and the intensity of the pain. You can also opt for cell-based therapy as a low-pain treatment for your knee issue.
Causes of Why You Can’t Straighten Your Knee
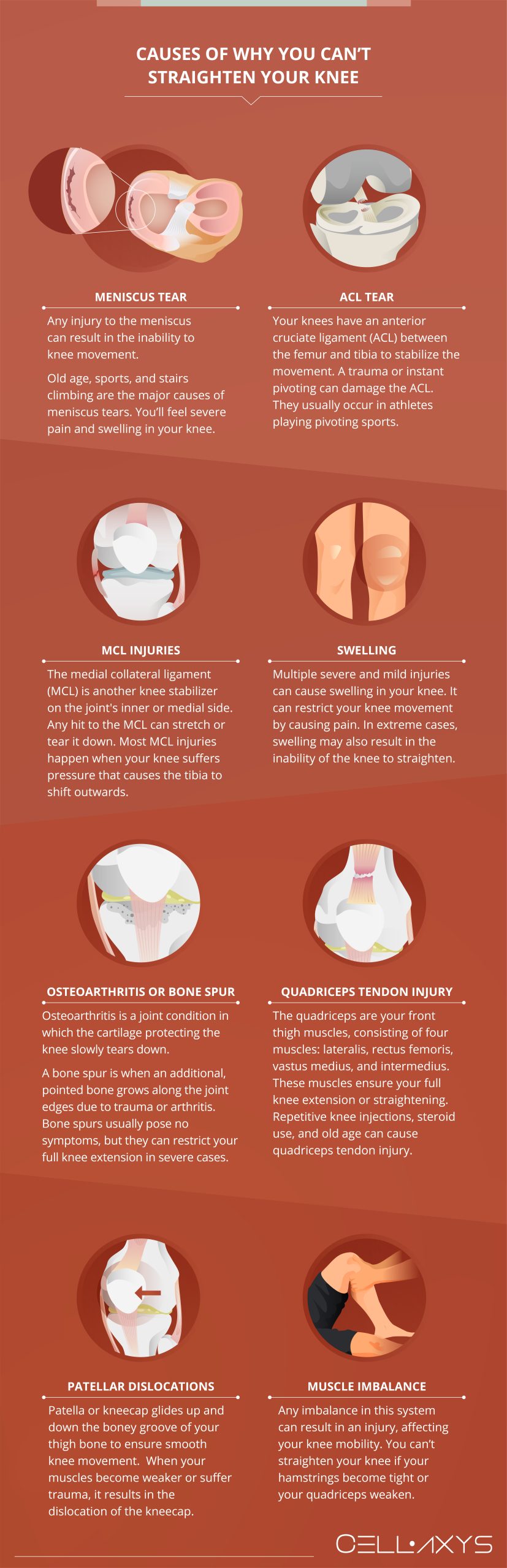
Multiple factors can’t restrict your knee movement. The primary causes include:
Meniscus Tear
You have two menisci in each knee. The meniscus is a crescent-shaped cushion between your shin bone (tibia) and thigh bone (femur). It absorbs shock and stabilizes your joints. Any injury to the meniscus can result in the inability to knee movement.
Old age, sports, and stair climbing are the major causes of meniscus tears. In case of meniscus injury, you’ll feel severe pain and swelling in your knee. As a result, you can’t straighten your knee.
ACL Tear
Your knees have an anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) between the femur and tibia to stabilize the movement. The ligament manages the forward and rotational movement of your knee. A trauma or instant pivoting can damage the ACL, resulting in restricted knee movement.
ACL tears usually occur in athletes playing pivoting sports. The most common symptoms include severe pain, rapid swelling, and failure to straighten the knee.
MCL Injuries
The medial collateral ligament (MCL) is another knee stabilizer on the joint’s inner or medial side. Any hit to the MCL can stretch or tear it down, causing severe pain. Most MCL injuries happen when your knee suffers pressure that causes the tibia to shift outwards.
Like ACL tears, athletes are also prone to MCL injuries, especially those who perform activities that include tackles.
Swelling
Multiple severe and mild injuries can cause swelling in your knee. It can restrict your knee movement by causing pain. In extreme cases, swelling may also result in the inability of the knee to straighten.
Osteoarthritis or Bone Spur
Osteoarthritis is a common form of arthritis, affecting more females than males. It is a joint condition where the cartilage protecting the knee slowly tears down, resulting in severe pain, swelling, and restricted mobility.
A bone spur or osteophyte is also a reason you can’t straighten the knee. It is when an additional, pointed bone grows along the joint edges due to trauma or arthritis. Bone spurs usually pose no symptoms, but they can restrict your full knee extension in severe cases.
Quadriceps Tendon Injury
The quadriceps are your front thigh muscles, consisting of four muscles: lateralis, rectus femoris, vastus medius, and intermedius. These muscles ensure your full knee extension or straightening. Repetitive knee injections, steroid use, and old age can cause quadriceps tendon injury.
It causes anterior knee pain that may restrict your knee movement.
Patellar Dislocations
The patella or kneecap glides up and down the bony groove of your thigh bone to ensure smooth knee movement. This groove is known as the trochlear groove. When your muscles become weaker or suffer trauma, it results in the dislocation of the kneecap.
Patellar dislocations affect more females, particularly those between the ages of 10 and 17.
Muscle Imbalance
You can locomote efficiently when your ligaments, tendons, and muscles move synchronously. For example, your lower leg muscles work together to enable your knee to extend and flex.
Any imbalance in this system can result in an injury, affecting your knee mobility. You can’t straighten your knee if your hamstrings become tight or your quadriceps weaken.
Treatment of Knee Issues
Knee injuries can quickly heal through lifestyle changes and non-invasive methods like cell-based therapies.
Lifestyle Changes
Some lifestyle changes include:
- Physical Exercises. Physical therapy is an easy way to strengthen muscles and recover body balance. Isometric and resistance exercises effectively build your ligaments, tendons, and cartilage.
- PRICE. Most specialists suggest PRICE to people with torn muscles. It includes protecting your knee from the possible causes of injuries (sports) or wearing protective gear, resting on the bed to support healing, doing icing and compression therapy to relieve the inflammation and swelling, and elevating your legs to regulate the blood flow.
- Proper Nutrition. Your diet should include nutrients and vitamins that accelerate the healing of your inflammation. Calcium, Vitamin C, D, and K, protein, zinc, magnesium, fiber, Omega-3s, and boron help build collagen and cartilage in your knees.
Cell-Based Therapy and Plasma-Rich Platelet (PRP) Therapy
If your pain doesn’t seem to lower with the above lifestyle changes, you can go for an orthobiologic procedure like cell-based therapies and plasma-rich platelet (PRP therapy. These methods focus on replacing your damaged tissues or cells with healthy ones.
Depending on your condition, your doctor may suggest one of the below types of cell-based or stem-cell therapy.
- Minimally Manipulated Adipose Tissue Transplant (MMAT). It includes replacing or transplanting your affected adipose tissues with new ones to rebuild the inflamed areas of your knees. If you need MMAT in several parts of your body, the doctor can perform all of them in the same procedure. You won’t need to go through separate procedures for every affected location.
- Bone Marrow Concentrate (BMAC). If you can’t straighten the knee due to a bone marrow defect, you may have to go through BMAC. This cell-based therapy replaces the affected cells of your bone marrow with healthier ones.
These procedures are usually performed within 1.5-2 hours. By the end, you may go home on an immediate basis.
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy focuses on stimulating the growth of healthy tissues. Your body needs platelets to attract healing cells in the blood and produce a sticky web called fibrin. The fibrin accelerates tissue development.
PRP is a popular orthobiologic treatment used for spine and orthopedic injuries. It typically takes 45 minutes to complete.
How Long Does it Take for Knee Injuries to Heal?
Every knee injury has a different healing duration. Generally, knee injuries can heal between 4 to 12 weeks, depending on your lifestyle changes and diet. If you exercise regularly, practice PRICE, and take proper anti-inflammatory nutrients, you will likely heal from a knee injury faster.
Sources
Footnotes
- Snoeker BA, Bakker EW, Kegel CA, Lucas C. Risk factors for meniscal tears: a systematic review including meta-analysis. The Journal of orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. 2013;43(6):352-67.
- Kim S, Bosque J, Meehan JP, Jamali A, Marder R. Increase in outpatient knee arthroscopy in the United States: a comparison of National Surveys of Ambulatory Surgery, 1996 and 2006. JBJS. 2011;93(11):994-1000.
- Heidari B. Knee osteoarthritis prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis and features: Part I. Caspian journal of internal medicine. 2011;2(2):205.
- Flanigan DC, Troyer J, Everhart JS, Uribe JW, Wherley E, Yagnik GP. Extensor mechanism injuries: quadriceps and patellar tendon ruptures. Orthopedic Surgery Clerkship: A Quick Reference Guide for Senior Medical Students. 2017;309-13.
- Jain NP, Khan N, Fithian DC. A treatment algorithm for primary patellar dislocations. Sports Health. 2011;3(2):170-4.
- Fleck SJ, Falkel JE. Value of resistance training for the reduction of sports injuries. Sports medicine. 1986;3:61-8.
- Partsch H. Compression therapy: clinical and experimental evidence. Annals of vascular diseases. 2012;5(4):416-22.
References
- Why Can’t I Straighten My Knee?. Verywell Health. Accessed 9/6/2023.
- Knock Knee. HSS. Accessed 9/6/2023.
- Kneecap Problems and Treatments. WebMD. Accessed 9/6/2023.
- 10 Supplements That Fight Inflammation. Healthline. Accessed 9/6/2023.
CELLAXYS does not offer Stem Cell Therapy as a cure for any medical condition. No statements or treatments presented by Cellaxys have been evaluated or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This site contains no medical advice. All statements and opinions are provided for educational and informational purposes only.
Dr Pejman Bady
Author
Dr. Pejman Bady began his career over 20 years ago in Family/Emergency Medicine, working in fast-paced emergency departments in Nevada and Kansas. He has served the people of Las Vegas as a physician for over two decades. Throughout this time, he has been met with much acclaim and is now the head of Emergency Medical Services in Nye County, Nevada. More about the doctor on this page.
Dr Pouya Mohajer
Contributor
Pouya Mohajer, M.D. is the Director of Spine and Interventional Medicine for CELLAXYS: Age, Regenerative, and Interventional Medicine Centers. He has over 20 years of experience in pain management, perioperative medicine, and anesthesiology. Dr. Mohajer founded and is the Medical Director of Southern Nevada Pain Specialists and PRIMMED Clinics. He has dedicated his career to surgical innovation and scientific advancement. More about the doctor on this page.