Published on: November 23, 2022 | Updated on: August 29, 2024
Pain in the lower back is pretty common among US adults, with about 80% of the population experiencing it at any point. When you stand up, your spine releases sudden pressure on the lower back muscles. As a result, they become tight and cause pain.
While pain is common in the elderly, it can also happen in young individuals. Many factors can cause lower back pain when standing up from a sitting position, including spinal stenosis, annular tears, ligament strains, etc.
Mild lower back pain isn’t something to worry about, as it can be treated with some at-home remedies. However, in severe cases, you may need proper clinical treatment.
Causes of Lower Back Pain When Standing Up
The lower back consists of facet joints that stay flexed and relaxed when sitting. But just as you stand up, the pressure compresses these joints. If you have arthritis or any other health condition, you may feel a sudden, sharp pain when standing up.
Here are some common causes of lower back pain when standing up from a sitting position:
Spondylolisthesis
Spondylolisthesis is when one vertebra moves forward from its original position to another. This shift occurs when you sit. When you stand up, the vertebrae take a few seconds to return to their original position for a few seconds. You may initially feel the pain during this period, but it will go away in a few seconds.
Annular Tear
The lumbar spine comprises five vertebral bodies. There are lumbar discs present between each vertebral body. Every disc has an outer fibrous ring called the annulus fibrosus, which covers the nucleus.
The annulus provides support, absorbs sudden forces, and ensures the spine’s stability. However, its fibers can damage or weaken through degeneration or trauma, causing annular tears. It is one of the major causes of lower back pain when standing up from a sitting position.
Degenerative Scoliosis
Degenerative scoliosis, or adult-onset scoliosis, is when the spine bends sideways. This bending is usually toward the right or left and can be severe, mild, or moderate. The curve is often in a “C” shape and is in the lower back.
Degenerative scoliosis results from the usual wear and tear of the discs, vertebral bodies, or small joints. In this condition, you may feel lower back pain when standing up from sitting.
Ehlers-Danlos Syndrome (EDS)
EDS is a genetic disorder with different signs and symptoms that vary depending on its type and severity. It most commonly impacts the blood vessels, skin, and joints. Your joints may feel hypermobile due to a defect in collagen formation.
EDS is also a primary reason for sudden lower back pain when standing up from a sitting position. However, since it’s hereditary, there is no particular cause for it.
Failed Back Surgery Syndrome (FBSS)
Failed back surgery syndrome (FBSS) is a clinical condition observed in patients who have undergone low back surgery and continue to have post-surgical pain. This means the surgery failed to reduce the patient’s pain and increased it. This condition is one of the most common causes of lower back pain when standing up.
Hamstrings Tendinopathy
The hamstrings are thick muscles in the back region of our thighs. They control the movement of our thighs, hips, and knees and are made of three muscles. These include Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, and Biceps Femoris. The muscles are connected to the bone through tendons, which are thick connective tissues.
Any strain or injury to the tendons results in hamstring tendinopathy. It is most apparent when you put pressure on your hamstrings when extending or bending your legs. Calf strain or pain is the most common symptom of hamstring tendinopathy.
SI Joint Syndrome
The sacrum and pelvic girdle consist of two sacroiliac (SI) joints. One is present on the right, while the other is on the left. The SI joints transfer back-and-forth forces through the spine and the lower limbs.
Any sudden trauma or fall can lead to SI joint syndrome, which causes severe pain and inflammation in the SI joints. With SI joint syndrome, you may feel sudden lower back pain when standing up from a sitting position.
Treatment Options for Lower Back Pain When Standing Up From Sitting Position
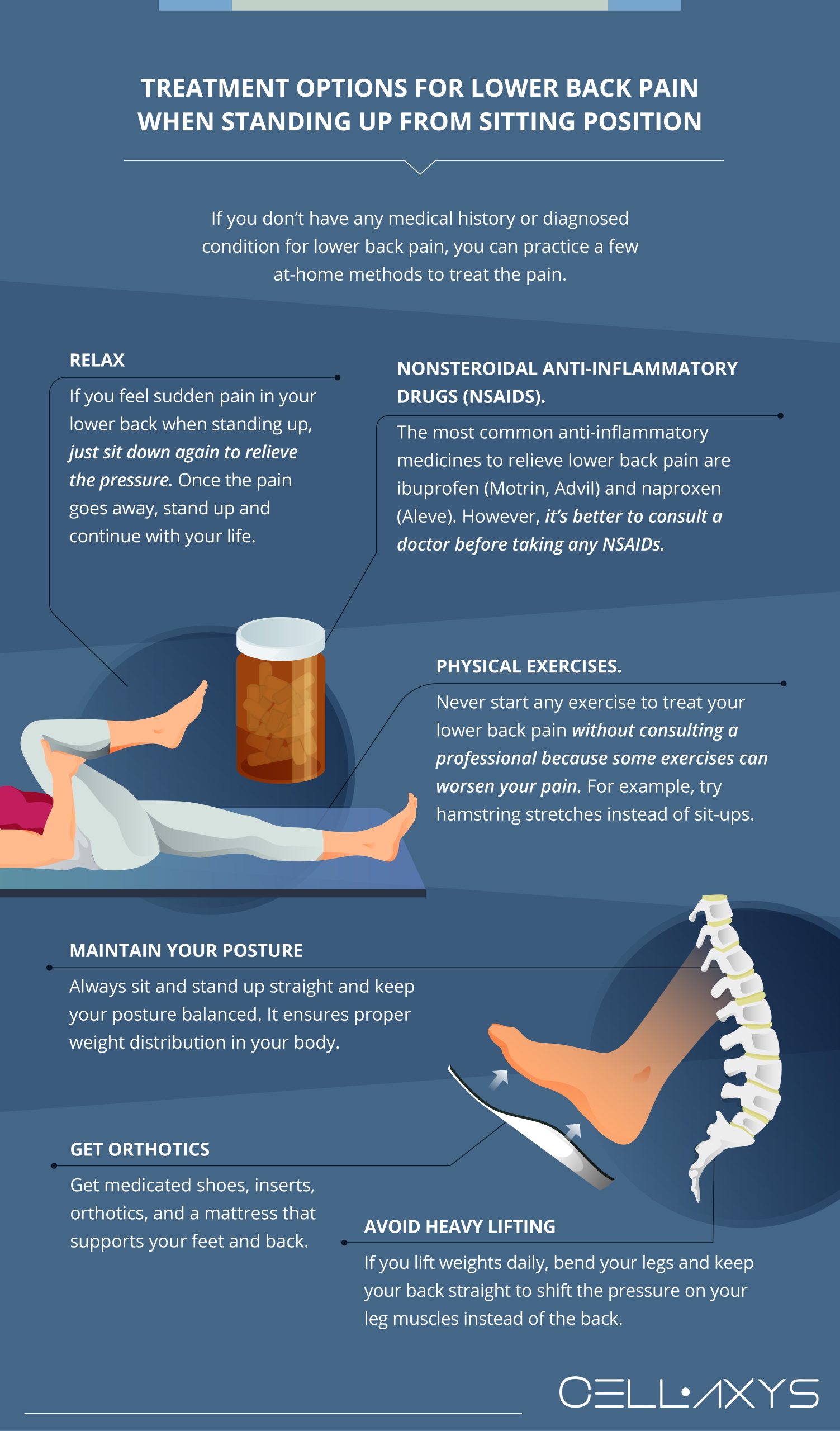
If you don’t have any medical history or diagnosed condition for lower back pain, you can practice a few at-home methods to treat the pain. Some conventional treatments include:
- Relax. If you feel sudden pain in your lower back when standing up, sit down again to relieve the pressure. Once the pain goes away, stand up and continue with your life.
- Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs). The most common anti-inflammatory medicines to relieve lower back pain include ibuprofen (Motrin, Advil) and naproxen (Aleve). However, it’s better to consult a doctor before taking any NSAIDs.
- Physical Exercises. Never start any exercise to treat your lower back pain without consulting a professional; some exercises can worsen your pain. For example, try hamstring stretches instead of sit-ups.
- Maintain Your Posture. Always sit and stand up straight, and keep your posture balanced. It ensures proper weight distribution in your body.
- Get Orthotics. Get medicated shoes, inserts, orthotics, and a mattress that supports your feet and back.
- Avoid Heavy Lifting. If you lift weights daily, bend your legs and keep your back straight to shift the pressure on your leg muscles instead of the back.
Orthobiologic Methods for Relieving Back Pain
If your lower back pain persists when standing up, you can try orthobiologic treatments to relieve the pain in a less painful and less invasive method. They are outpatient procedures, meaning you won’t have to spend a night at the clinic.
At CELLAXYS, we perform two types of treatments:
Cell-based Therapies
These are also known as stem-cell therapies. The procedure includes harvesting the patient’s healthy “autologous” cells, processing them, and reinjecting them into the injury site. The doctor may opt for any of the below cell-based therapies:
- Minimally Manipulated Adipose Tissue (MMAT) Transplant. This process extracts cells from your adipose (fat) tissue.
- Bone Marrow Concentrate (BMAC). This process extracts highly concentrated cells from your bone marrow.
Both MMAT and BMAC take about 1.5 to 2 hours to complete.
Platelet-Rich Plasma Therapy (PRP)
PRP includes taking the patient’s blood sample, isolating platelets, and reinjecting them into the injury site. Platelets are the healing elements of the human body. They release 10 Growth Factors, attract healing cells from the blood, and produce fibrin to promote the development of new tissues.
A high number of platelets in the injury site boosts healing and recovery. PRP is completed in 45 minutes.
Sources
Footnotes
- Snoeker BA, Bakker EW, Kegel CA, Lucas C. Risk factors for meniscal tears: a systematic review including meta-analysis. The Journal of orthopaedic and sports physical therapy. 2013;43(6):352-67.
- Kim S, Bosque J, Meehan JP, Jamali A, Marder R. Increase in outpatient knee arthroscopy in the United States: a comparison of National Surveys of Ambulatory Surgery, 1996 and 2006. JBJS. 2011;93(11):994-1000.
- Heidari B. Knee osteoarthritis prevalence, risk factors, pathogenesis and features: Part I. Caspian journal of internal medicine. 2011;2(2):205.
- Flanigan DC, Troyer J, Everhart JS, Uribe JW, Wherley E, Yagnik GP. Extensor mechanism injuries: quadriceps and patellar tendon ruptures. Orthopedic Surgery Clerkship: A Quick Reference Guide for Senior Medical Students. 2017;309-13.
- Jain NP, Khan N, Fithian DC. A treatment algorithm for primary patellar dislocations. Sports Health. 2011;3(2):170-4.
- Fleck SJ, Falkel JE. Value of resistance training for the reduction of sports injuries. Sports medicine. 1986;3:61-8.
- Partsch H. Compression therapy: clinical and experimental evidence. Annals of vascular diseases. 2012;5(4):416-22.
References
- Why Can’t I Straighten My Knee?. Verywell Health. Accessed 9/6/2023.
- Knock Knee. HSS. Accessed 9/6/2023.
- Kneecap Problems and Treatments. WebMD. Accessed 9/6/2023.
- 10 Supplements That Fight Inflammation. Healthline. Accessed 9/6/2023.
CELLAXYS does not offer Stem Cell Therapy as a cure for any medical condition. No statements or treatments presented by Cellaxys have been evaluated or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This site contains no medical advice. All statements and opinions are provided for educational and informational purposes only.
Dr Pouya Mohajer
Author
Pouya Mohajer, M.D. is the Director of Spine and Interventional Medicine for CELLAXYS: Age, Regenerative, and Interventional Medicine Centers. He has over 20 years of experience in pain management, perioperative medicine, and anesthesiology. Dr. Mohajer founded and is the Medical Director of Southern Nevada Pain Specialists and PRIMMED Clinics. He has dedicated his career to surgical innovation and scientific advancement. More about the doctor on this page.
Dr Pejman Bady
Contributor
Dr. Pejman Bady began his career over 20 years ago in Family/Emergency Medicine, working in fast-paced emergency departments in Nevada and Kansas. He has served the people of Las Vegas as a physician for over two decades. Throughout this time, he has been met with much acclaim and is now the head of Emergency Medical Services in Nye County, Nevada. More about the doctor on this page.