Published on: April 5, 2024 | Updated on: January 18, 2025
Carpal tunnel syndrome and wrist tendonitis are recurring wrist conditions in people who use their fingers or wrists daily. If you’re a cashier or a grocery store clerk, know that you can develop either of the conditions anytime.
Carpal tunnel and tendonitis can lead to chronic pain in the wrist and hand. It may also cause tingling in the fingers, making it hard to continue your work.
Many people think both conditions are two names of the same issue, but they do differ in terms of symptoms. Your healthcare provider can quickly diagnose whether you have carpal tunnel syndrome or tendonitis.
However, if you want to learn how to differentiate between both, keep reading this post till the end. We will also tell you about two surgical alternatives that can treat both these conditions in less pain.
What Is Wrist Tendonitis?
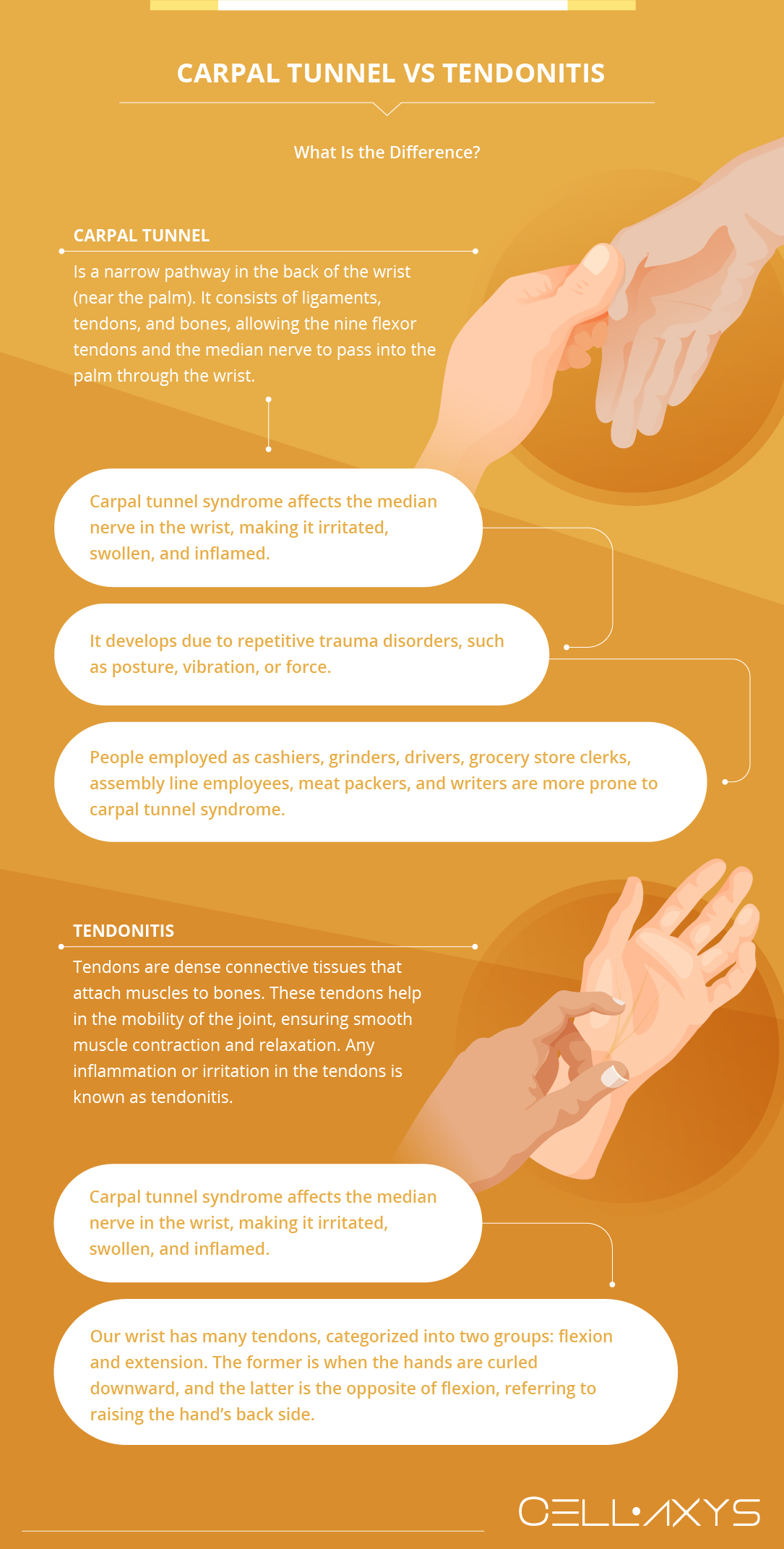
Tendons are dense connective tissues that attach muscles to bones. These tendons help in the mobility of the joint, ensuring smooth muscle contraction and relaxation. Any inflammation or irritation in the tendons is known as tendonitis.
Our wrist has many tendons, categorized into two groups: flexion and extension. The former is when the hands are curled downward, and the latter is the opposite of flexion, referring to raising the hand’s back side.
The flexor tendons are present in the wrist’s underside or palm area. They include flexor carpi ulnaris (FCU), flexor carpi radialis (FCR), and palmaris longus (PL). Meanwhile, the extensor tendons are on the wrist’s backside where the knuckles are. They are divided into six groups, differentiated by Roman numbers: I, II, III, and continued.
Every group or compartment is like a tunnel containing one or more extensor tendons.
Causes of Wrist Tendonitis
Inflammation in your wrist tendons can occur anytime due to many reasons. These include the following:
- Repetitive motion injuries, including writing, typing, texting, or playing a musical instrument
- Trauma
- Weak wrists
- Damaged wrist ligaments
- Improper bone positioning in the wrist
- Arthritis
- Diabetes
- Increased BMI or overweight individuals
Symptoms of Wrist Tendonitis
Wrist tendonitis causes instant pain in the affected tendon. If left untreated, the pain can get worse with activity. Some common wrist tendonitis symptoms include:
- Swelling in the tendons
- Redness or bruising
- Popping or clicking sounds when moving wrists
What Is Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
The carpal tunnel is a narrow pathway in the back of the wrist (near the palm). It consists of ligaments, tendons, and bones, allowing the nine flexor tendons and the median nerve to pass into the palm through the wrist.
Carpal tunnel syndrome affects the median nerve in the wrist, making it irritated, swollen, and inflamed. Carpal tunnel syndrome is a painful nerve condition that affects 20% of adults, around one million in the USA annually.
It develops due to repetitive trauma disorders, such as posture, vibration, or force. People employed as cashiers, grinders, drivers, grocery store clerks, assembly line employees, meat packers, and writers are more prone to carpal tunnel syndrome.
Causes of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused due to local, regional, and systemic factors. Below are the most common causes of this wrist condition:
- Trauma
- Osteoarthritis
- Gout
- Diabetes
- Obesity
- Low thyroid
- Pregnancy
- Rheumatoid arthritis (RA)
- Tumors that compress the median nerve
- Inflammation in tendons and synovium (surrounding sheaths)
- Autoimmune disorders like lupus, sarcoidosis, and scleroderma
Symptoms of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome leads to different symptoms in every individual, depending on the severity of the nerve compression. In most cases, the symptoms may gradually develop in both wrists, fingers, and thumb.
Some people may also experience burning pain and headaches with carpal tunnel syndrome. Other symptoms of this condition include:
- Sudden pain or numbness in the wrist that goes away with shaking the hand
- Needle sensations in fingers and wrists, also called nighttime pins
- Clumsiness in hands
- Weakness in wrists or hands
- Swelling in the hand and fingers
Carpal Tunnel vs Tendonitis: The Differences
The differences between both carpal tunnel and tendonitis are quite visible by now. Yes, both conditions have similar symptoms, but they usually vary in terms of the causes.
Tendonitis occurs due to inflammation in the wrist tendons, while carpal tunnel syndrome’s symptoms result from the compression of the median nerve in the wrist. You can easily differentiate between both conditions from the pain location.
Wrist tendonitis is indicated by pain on the wrist’s top and muscle weakness. On the other hand, carpal tunnel syndrome occurs in the palm side of the wrist, causing numbness and tingling in the thumb and middle and index fingers.
Treatment Options for Carpal Tunnel and Tendonitis
The treatment for both carpal tunnel and tendonitis is almost similar. They are treated with conservative care to either relieve the tendon inflammation or the nerve compression.
Conventional Methods
The first-line treatment for carpal tunnel and tendonitis includes:
-
- A Splint. Limit your work when you experience slight pain or discomfort in your wrists, and opt for a splint.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications. Your doctor may suggest quality turmeric and fish oil medications to relieve the inflammation. Never use nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) without your doctor’s prescription, as Aleve and Motrin can lead to heart attack or gut damage.
- Physical Therapy. You may be advised to stretch your tight muscles and strengthen the wrist joint. For carpal tunnel syndrome, carpal bone mobilization, nerve glides, and yoga may give short-term benefits.
- Injections. If none of the above methods work, the doctor may opt for steroid injections to reduce the inflammation. Some helpful options include Hydrocortisone, Dexamethasone, and Betamethasone. It’s worth noting that steroid injections can damage your tendons, so they are administered with great care.
Surgery
Wrist tendonitis rarely requires any surgery, but it is the last resort for carpal tunnel syndrome if conservative care fails.
The surgery for carpal tunnel syndrome involves cutting the carpal tunnel’s roof that’s made of the transverse carpal ligament. This relieves the compressed median nerve. The surgery can be performed open, using a cutting instrument, or endoscopically.
Nerve hydro dissection is a modern solution that cuts the transverse ligaments to free up the scar tissue around the median nerve.
Orthobiologic Methods
For persistent pain in carpal tunnel syndrome and tendonitis, orthobiologic treatments like cell-based therapies (stem cell therapy) and PRP therapy are the best solutions. At CELLAXYS, our board-certified surgeons perform these methods with great care and supervision.
- Cell-based Therapies. This procedure involves extracting healthy cells from the patient’s adipose (fat) tissues (Minimally Manipulate Adipose Tissue Transplant MMAT) or bone marrow (Bone Marrow Concentrate BMAC) and reinjecting them into the injury site. Cell-based therapies take about 1.5 to 2 hours to complete.
- Platelet-rich Plasma (PRP) Therapy. In PRP, the surgeon takes the patient’s blood sample, separates platelets from it, and reinjects them into the injury site. Platelets are the healing components of our body, releasing 10 growth factors, attracting healing cells, and producing web-like scaffolding called fibrin. PRP takes 45 minutes and is a popular treatment for spine, sports, and orthopedic injuries.
Cell-based therapies and PRP are outpatient procedures, meaning you can go home right after the treatment. People with carpal tunnel syndrome or wrist tendonitis report quick recovery with less pain.
Sources
Footnotes
- Thorson EP, Szabo RM. Tendonitis of the wrist and elbow. Occupational Medicine (Philadelphia, Pa.). 1989;4(3):419-31.
- Genova A, Dix O, Saefan A, Thakur M, Hassan A. Carpal tunnel syndrome: a review of literature. Cureus. 2020;12(3).
- Atroshi I, Gummesson C, Johnsson R, Ornstein E, Ranstam J, Rosén I. Prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome in a general population. JAMA. 1999;282(2):153-8.
- Tanaka S, Wild DK, Seligman PJ, Behrens V, Cameron L, Putz-Anderson V. The US prevalence of self-reported carpal tunnel syndrome: 1988 National Health Interview Survey data. American Journal of Public Health. 1994;84(11):1846-8.
- Padua L, Padua R, Nazzaro M, Tonali P. Incidence of bilateral symptoms in carpal tunnel syndrome. The Journal of Hand Surgery: British & European Volume. 1998;23(5):603-6.
- Akalin E, El Ö, Peker Ö, Senocak Ö, Tamci S, Gülbahar S, Çakmur R, Öncel S. Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome with nerve and tendon gliding exercises. American journal of physical medicine & rehabilitation. 2002;81(2):108-13.
References
- Signs of Carpal Tunnel Syndrome & Tendinitis. CarpalRX. Accessed 11/5/2023.
- Carpal tunnel vs tendinitis: What’s the difference?. Alliance Physical Therapy Partners. Accessed 11/5/2023.
- Carpal Tunnel vs. Tendonitis: Similarities And Differences. Midwest Hand Surgery. Accessed 11/5/2023.
CELLAXYS does not offer Stem Cell Therapy as a cure for any medical condition. No statements or treatments presented by Cellaxys have been evaluated or approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA). This site contains no medical advice. All statements and opinions are provided for educational and informational purposes only.
Dr Pejman Bady
Author
Dr. Pejman Bady began his career over 20 years ago in Family/Emergency Medicine, working in fast-paced emergency departments in Nevada and Kansas. He has served the people of Las Vegas as a physician for over two decades. Throughout this time, he has been met with much acclaim and is now the head of Emergency Medical Services in Nye County, Nevada. More about the doctor on this page.
Dr Pouya Mohajer
Contributor
Pouya Mohajer, M.D. is the Director of Spine and Interventional Medicine for CELLAXYS: Age, Regenerative, and Interventional Medicine Centers. He has over 20 years of experience in pain management, perioperative medicine, and anesthesiology. Dr. Mohajer founded and is the Medical Director of Southern Nevada Pain Specialists and PRIMMED Clinics. He has dedicated his career to surgical innovation and scientific advancement. More about the doctor on this page.